Modern vehicles rely on complex powertrain systems that integrate multiple components to generate and transfer mechanical energy. The powertrain is a comprehensive network of interconnected parts responsible for converting fuel or electrical energy into vehicle movement, with the engine serving as the primary power generation unit. Understanding the relationship between the engine and powertrain is crucial for comprehending automotive mechanical systems.
What Exactly is a Powertrain?
A powertrain represents the complete set of components that generate and transmit mechanical power from the initial energy source to the vehicle’s wheels. This intricate system encompasses several critical elements:
Key Powertrain Components
| Component | Primary Function | Power Transmission Role |
|---|---|---|
| Engine | Power generation | Converts chemical/electrical energy to mechanical energy |
| Transmission | Power regulation | Adjusts engine output for different driving conditions |
| Driveshaft | Power transfer | Connects transmission to differential |
| Differential | Power distribution | Allows wheels to rotate at different speeds |
| Axles | Power delivery | Transfers rotational energy to wheels |
Does the Engine Constitute Part of the Powertrain?
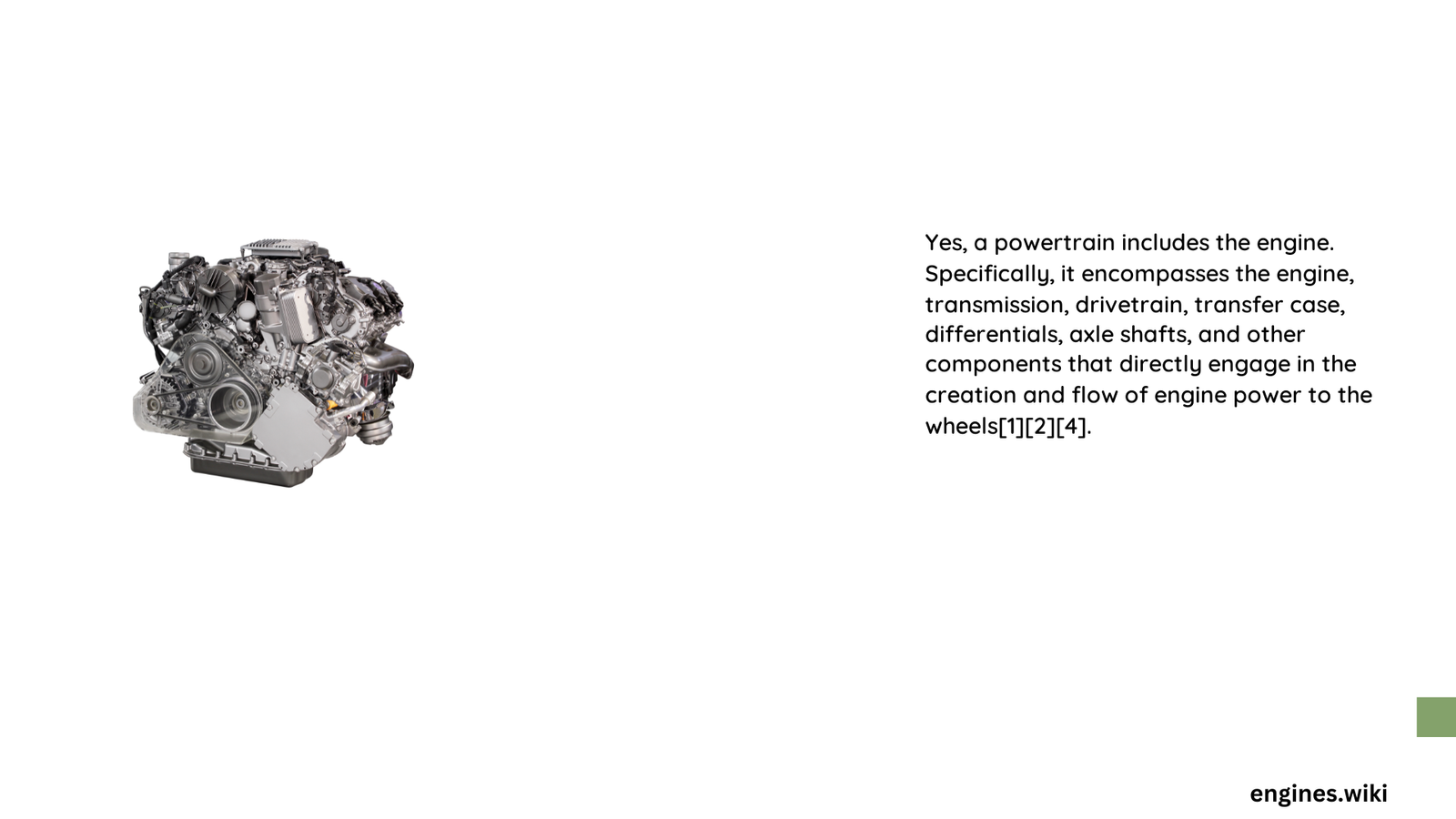
Absolutely, the engine is the central component of the powertrain. It serves as the primary power generation unit, converting fuel or electrical energy into mechanical motion. Without the engine, the powertrain cannot function.
Engine Types in Modern Powertrains
- Internal Combustion Engines
- Gasoline engines
- Diesel engines
-
High-performance variants
-
Electric Powertrains
- Battery electric motors
- Hybrid electric systems
- Fuel cell electric configurations
How Do Powertrain Components Interact?
The powertrain operates as an integrated system where each component plays a crucial role:
- Engine generates initial power
- Transmission modulates power output
- Driveshaft transfers rotational energy
- Differential distributes power to wheels
Power Transmission Sequence
Engine → Transmission → Driveshaft → Differential → Wheels
Technical Considerations in Powertrain Design
Powertrain engineering involves complex considerations:
- Efficiency optimization
- Weight reduction
- Thermal management
- Emissions control
- Performance enhancement
Emerging Powertrain Technologies
Modern automotive engineering is rapidly evolving, with emerging powertrain technologies:
- Electric vehicle platforms
- Hybrid propulsion systems
- Advanced transmission designs
- Lightweight materials
- Intelligent power management systems
Performance and Efficiency Metrics
Powertrain performance is evaluated through:
- Horsepower
- Torque
- Fuel efficiency
- Emissions output
- Durability
Conclusion
The engine is unequivocally a fundamental component of the powertrain. It represents the primary power generation unit that enables vehicle movement, working in concert with transmission, driveshaft, differential, and axle systems to deliver mechanical energy to the wheels.
Expert Insights
Vehicle engineers emphasize that modern powertrains are increasingly sophisticated, integrating advanced technologies to improve overall system efficiency and performance.
Reference:
– SAE International
– Society of Automotive Engineers
– National Renewable Energy Laboratory
