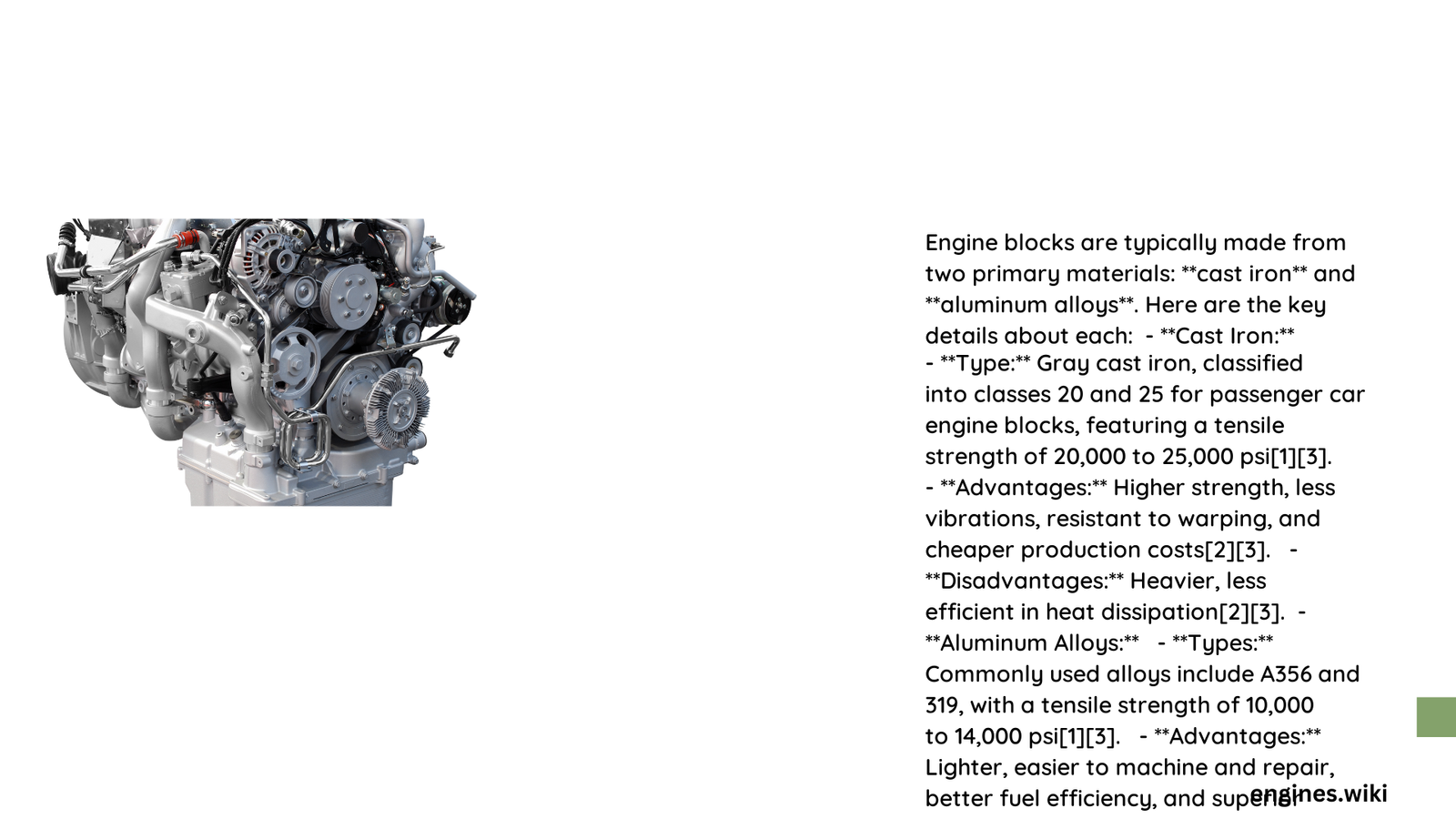
Engine blocks are the foundational structural component of internal combustion engines, serving as the critical housing for cylinders, coolant passages, and critical mechanical systems. Modern automotive engineering utilizes multiple materials with unique performance characteristics, each offering distinct advantages in weight, strength, thermal management, and manufacturing complexity. Understanding these materials is essential for engineers, automotive designers, and performance enthusiasts seeking optimal engine design solutions.
What Are the Primary Materials for Engine Block Construction?
Why Choose Aluminum for Engine Blocks?
Aluminum engine blocks represent a modern engineering solution characterized by exceptional weight reduction and thermal performance. Key specifications include:
| Property | Aluminum Specification |
|---|---|
| Weight Reduction | 30% lighter than cast iron |
| Tensile Strength | 10,000-14,000 psi |
| Thermal Conductivity | 150-200 W/m·K |
Advantages of Aluminum Blocks:
– Superior weight-to-strength ratio
– Enhanced heat dissipation
– Improved fuel efficiency
– Corrosion resistance
Manufacturing Challenges:
– Higher production costs
– Requires advanced reinforcement techniques
– More susceptible to thermal stress
How Do Cast Iron Engine Blocks Compare?
Cast iron remains a traditional and robust material for engine block construction, offering unique mechanical properties:
Technical Characteristics:
– Higher tensile strength (20,000-25,000 psi)
– Excellent pressure resistance
– Lower thermal expansion
– Superior vibration damping
Performance Considerations:
– Heavier compared to aluminum
– More cost-effective manufacturing
– Better noise absorption
– Enhanced durability under extreme conditions
What Role Do Composite Materials Play?
While not mainstream, composite materials represent an emerging technology in engine block design:
Innovative Features:
– Extreme weight reduction
– Customizable mechanical properties
– High-performance specialized applications
– Advanced material engineering
Implementation Limitations:
– Expensive manufacturing processes
– Complex production techniques
– Limited widespread adoption
What Factors Influence Material Selection?
Performance Criteria
- Thermal management
- Structural integrity
- Manufacturing complexity
- Cost considerations
- Application-specific requirements
Engineering Trade-offs
- Weight reduction vs. structural strength
- Manufacturing costs
- Thermal performance
- Long-term durability
- Application-specific demands
What Emerging Technologies Are Shaping Engine Block Materials?
Advanced Development Trends
- Hybrid material compositions
- Nanotechnology integration
- Advanced computational modeling
- Additive manufacturing techniques
Future Potential
- Lighter, more efficient designs
- Enhanced thermal management
- Improved performance characteristics
- Sustainable manufacturing processes
Conclusion
The selection of engine block materials represents a complex engineering decision balancing multiple technical parameters. While aluminum and cast iron remain dominant, emerging composite technologies promise exciting future developments in automotive engineering.
